Remote content & data
#Overview
Remote Fields are fields that you can add to a model in order to fetch data from a remote source. There are two types:
- Remote Field: A field inside a regular Hygraph model that connects specific remote data to an entry of that model. Remote Fields are always related to a single remote source, and a single custom type. RESTful remote fields are configured with a path to a specific endpoint in the remote source, such as user details from Github, or price & availability from Shopify.
- Top Level Remote Field: A field inside the
Querysystem model in Hygraph. These fields are used to fetch remote data outside the context of a regular model, which is then sent to your frontend alongside your Hygraph data. This Content Federation utility eliminates the need to make separate API requests for data inside & outside of Hygraph.
#Remote Fields vs Top Level Remote Fields
You can use Remote Fields to enrich data by fetching information from a Remote Source. This data can be queried in the context of the model it's a part of.
Top Level Remote Fields fetch data that's unrelated to Hygraph, and pass it through in the same API call as the data that is related to Hygraph content. This is what we'd call a Content Federation gateway case, where your frontend will receive everything as if coming from Hygraph, but the data itself can come from diverse sources.
#Adding remote data to your model
This document section explains how to add Remote Fields to models in your project. The flow is the same for Remote Fields added to regular models, and Top Level Remote Fields.
Here is an explanation on how they are different from each other.
After adding a Remote Source, it's now time to add a Remote Field to a model. This is slightly different for RESTful remote sources vs. GraphQL Remote Sources, so we will explain this step for each of them separately.
Note that Remote Fields can only be added after at least one Remote Source of the corresponding type has been configured.
#REST
First, select a Remote Field type:
- If you're adding a Remote Field to a regular model: Navigate to the Schema builder, select the model that will contain your Remote Field, scroll down the field type list located on the right side of the screen, and select the REST field.
- If you're adding Top Level Remote Fields: Navigate to the
Querymodel in your project schema, then select the REST field from the Add fields list located on the right side of the screen.
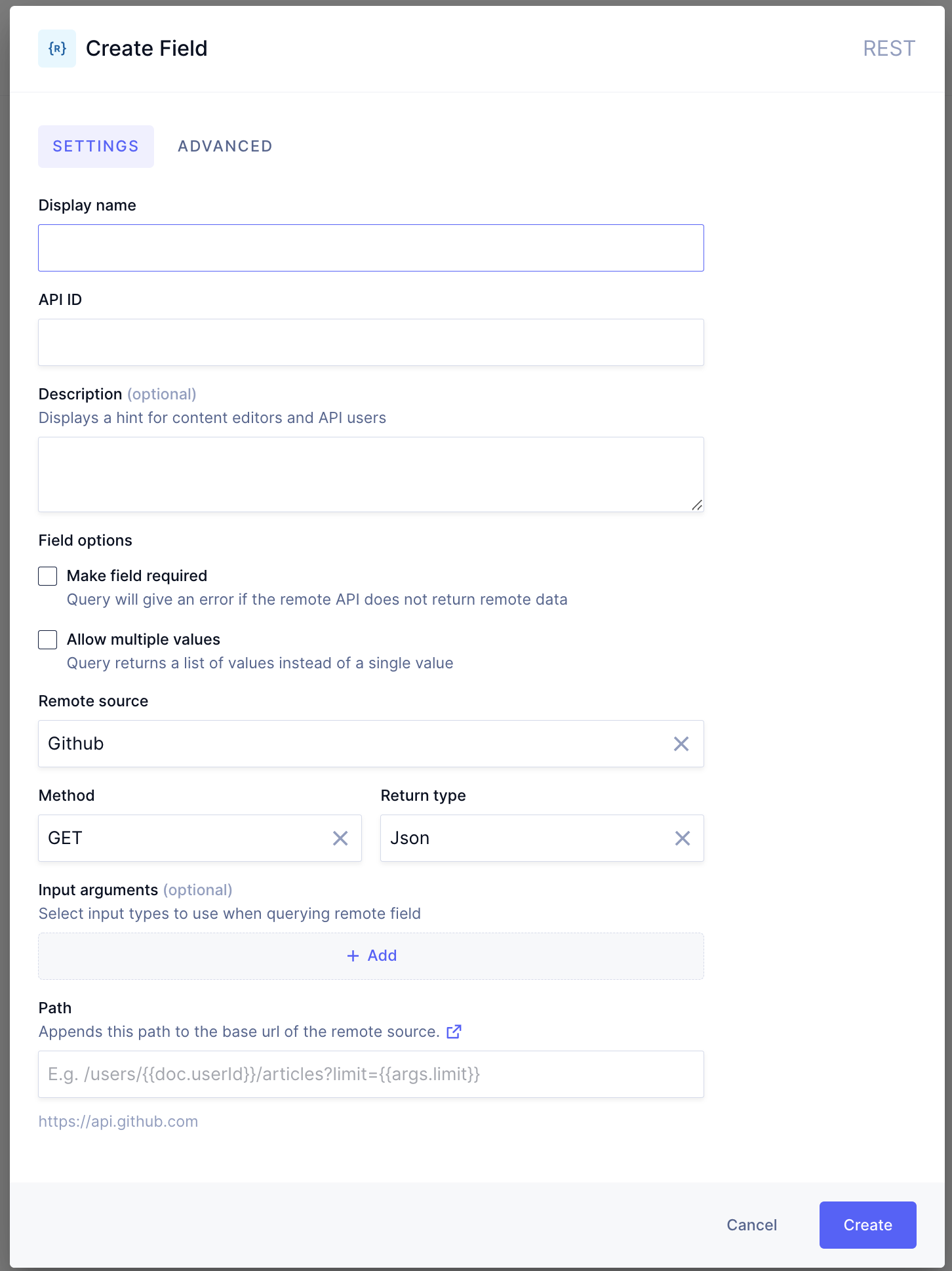 Creating a REST Remote Field
Creating a REST Remote Field
Then, follow these instructions:
- In the
Create Fielddialog, fill in theDisplay name,API ID, and optionally add aDescription. - If the remote API for this field returns an array of the chosen custom type instead of a single object, make sure to select the
Allow multiple valuescheckbox, underField options. For instance, if you defined your custom type to beProduct, but the remote API returns an array of products, you need to make use of theAllow multiple valuesoption, so the request won't return an error. - Select a previously configured
Remote sourceand an HTTPMethodusing the dropdowns. ForReturn type, select one of the custom types that you configured for the Remote Source. This custom type needs to (partially) match with the response of the API path that will be requested in this field. You can find detailed information on creating custom types here. Alternatively, it's possible to set the response to be a scalar type (string, Boolean, Json, etc). - You can optionally add
Input arguments. Adding an input argument is done by providing anapiIdfor the inputs (which can be used in the configuration of the URL path), and selecting a previously configured custom input type for the remote source. Multiple input arguments can be added by clicking on+Add. We understand this is a difficult step, so we've provided an example below for more details. - Configure the
Paththat will be queried for this Remote Field. This path will be added to the Remote Source base path to get a resulting endpoint. In the path definition, you can use handlebars notation (start by typing a{) to use fields from the document or from the input arguments, if defined. This way, you can dynamically build a URL path using field values from the same content model or from an input parameter value. As an example, if the model has a field calleduserId, it's possible to build a path that looks like this:/users/{{doc.userId}}/repos.
#GraphQL
First, select a Remote Field type:
- If you're adding a Remote Field: Navigate to the Schema builder, select the model that will contain your Remote Field, scroll down the field type list located on the right side of the screen, and select the GraphQL field.
- If you're adding Top Level Remote Fields: Navigate to the
Querymodel in your project schema, then select the GraphQL field from the Add fields list located on the right side of the screen.
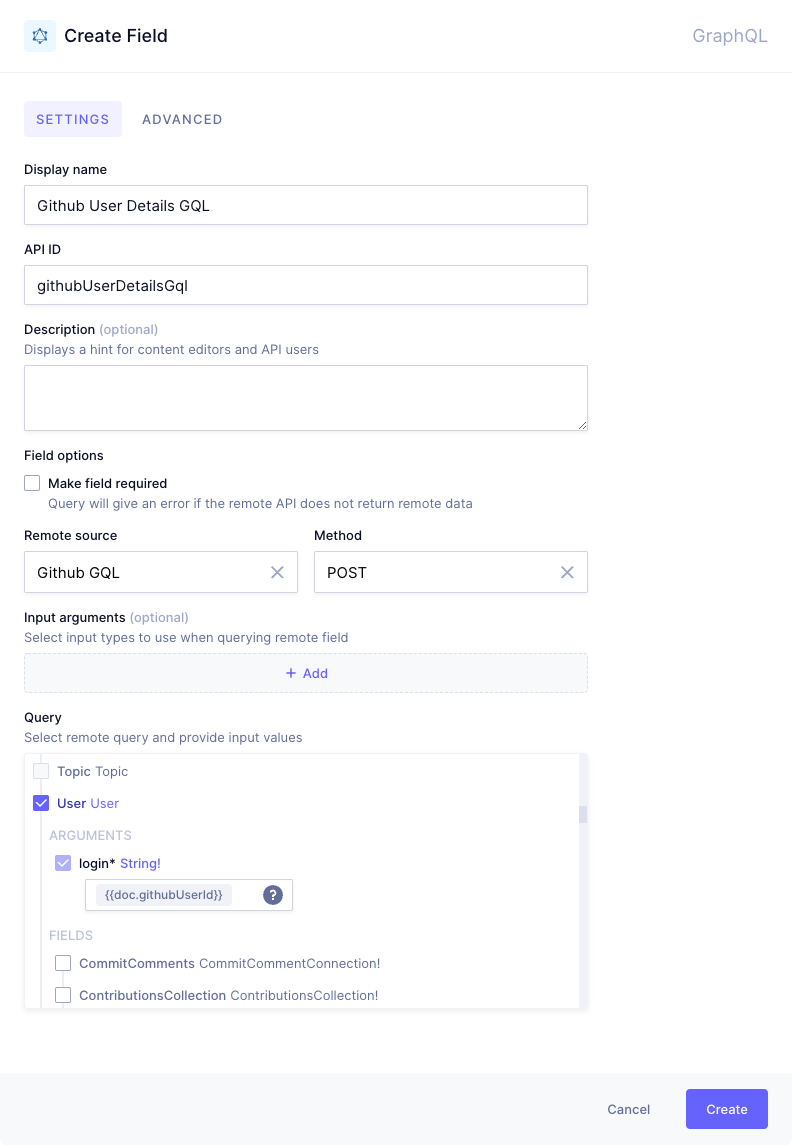 Creating a GraphQL Remote Field
Creating a GraphQL Remote Field
Then, follow these instructions:
-
In the
Create Fielddialog, fill inDisplay name,API ID, and optionally add aDescription. -
Select a previously configured
Remote Sourceand an HTTPMethod. -
You can optionally add
Input arguments. Adding an input argument is done by providing anapiIdfor the inputs (which can be used in the configuration of the URL path), and selecting a previously configured custom input type for theRemote Rource. Multiple input arguments can be added by clicking on+Add. We understand this is a difficult step, so we've provided an example below for more details. -
Now select the
Querythat will be the entry point into the remote schema from the tree that is shown at the bottom of theCreate Fielddialog. This tree is populated using introspection, and will show all available queries in the Remote Source.-
When selecting a query, the tree unfolds to show all arguments for that query (in purple), available sub-queries (enabled and showing type in blue), and available fields or scalars (disabled and showing with type in grey). It's important to note that the selected (sub)query will determine which data from the remote source can be queried through Hygraph. All arguments, scalars, and subqueries in the Remote Source that are below the selected query will be queryable. Other values and queries in the tree will not be queryable unless they are part of another Remote Field.
-
Arguments that are required show a purple asterisk (*) next to their ID, although there is no validation on the value done inside Hygraph. It's possible to use handlebars notation inside a parameter field. Start by typing
{, which will bring up suggestions based on the fields on your model.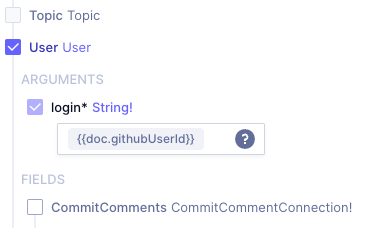 Selecting the Schema entrypoint
Selecting the Schema entrypoint -
For queries that return a single value, it's also possible to select a sub-query as the entry point. Note that this means that only fields inside the selected sub-query are available to be queried through Hygraph.
-
#Errors
Irrespective of the model you selected, the default behavior for errors in querying Remote Fields is that the query to Hygraph will return successfully but with a null value for the Remote Field and an error message to indicate the Remote Field could not be queried. If the value of the Remote Field is critical for the proper functioning of the front-end application, it's possible to mark the Remote Field as required. With this setting enabled, the whole query to Hygraph will return an error if the Remote Field does not provide a successful response.
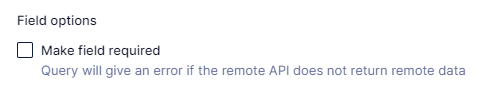 Remote Field required constraint
Remote Field required constraint
#Advanced settings (Cache)
Note that advanced settings apply to both types of Remote Fields
- Although HTTP headers can be configured on a remote source - meaning on all requests for all fields that use this remote source - it's also possible to add additional HTTP headers on a specific remote field. The headers are additive, but if you configure the same header both on the field and on the remote source, the value from the Remote Field will take precedence. Additionally, it's possible to have all client headers to Hygraph forwarded to the Remote Source. This can be useful to forward user context to the remote server, for example.
- By default, Hygraph caches queries that include Remote Fields using a TTL cache with a value of 15 minutes. The TTL can be overridden in the Remote Field settings dialog (minimum TTL value is 60 seconds). However, please note that if the Remote Source sends a cache-control response header, this will override the cache configuration in Hygraph.
- Optionally set field visibility. For the default setting of
read-only, the Remote Field is displayed in the content form with a link to the API playground. If the field visibility is set toAPI only, the Remote Field is not displayed in the content form but is still available to query through the API.
#Remote Fields
Remote Fields are fields inside a Hygraph model that connect specific remote data to an entry of that model.
These fields are always related to a single Remote Source, and a single custom type. RESTful Remote Fields are configured with a path to a specific endpoint in the Remote Source, such as user details from Github, or price & availability from Shopify.
#What you can do with Remote Fields
You can add Remote Fields to regular models in your schema to enrich data.
#Possible use cases for Remote Fields
- They can facilitate e-commerce by consolidating product listings from multiple suppliers onto one platform.
- In travel, they can integrate flight, hotel, and rental car information from numerous providers.
- In stock management, they can provide real-time inventory data from various warehouses, enabling efficient tracking and management.
#Add Remote Fields
- If you don't already have one, create a Remote Source by following our Remote Sources creation flow.
- Navigate to your project schema and select the model you want to add the Remote Field to.
- Add a Remote Field to your model by following the Adding remote data to your model flow.
#Query Remote Fields
After configuring the Remote Field, it's added to the Hygraph schema and immediately queryable through the API. Press CTRL/CMD+Space or open the Explorer view to see the available sub-fields inside the Remote Field.
Note that the Remote Source prefix is added in front of the type for easy identification.
Below screenshots demonstrate what this looks like for the User endpoint of the Github API:
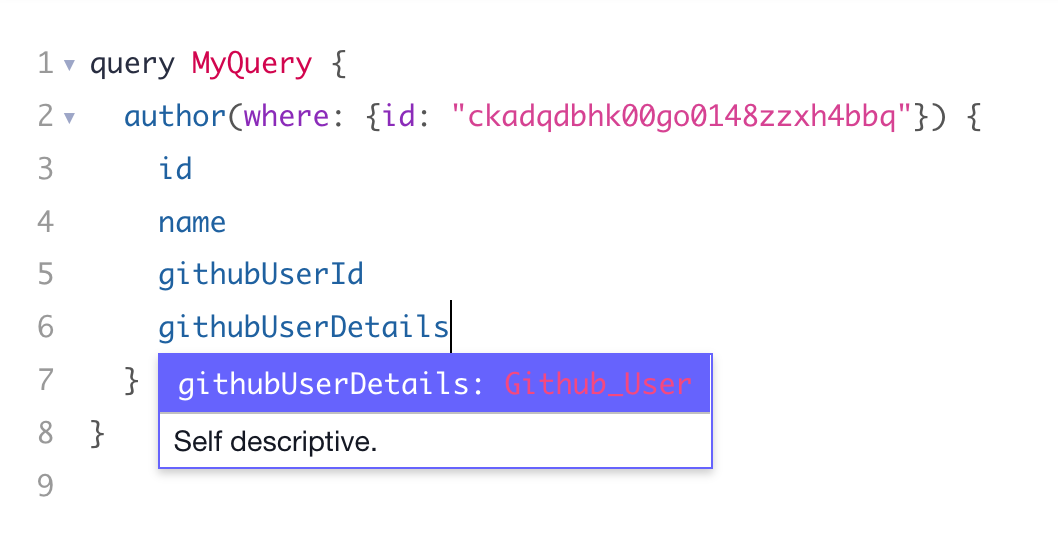 Querying a Remote Field
Querying a Remote Field
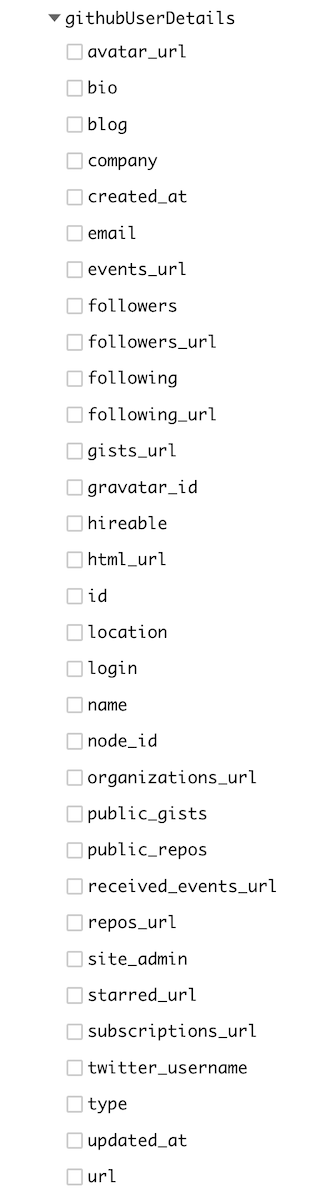 API Playground Explorer
API Playground Explorer
The following example fetches information from within a model:
In this case, the Remote Field is related to the Products model, and it only fetches data related to it.
#Example: Remote Field
This example shows a product content entry that fetches the product catalogue from a Remote Source.
Besides the data that lives in Hygraph inside a regular model called Product - Product name, product description, etc - you can fetch a product catalogue from an external API through a remote source that you added to the Product model as a Remote Field.
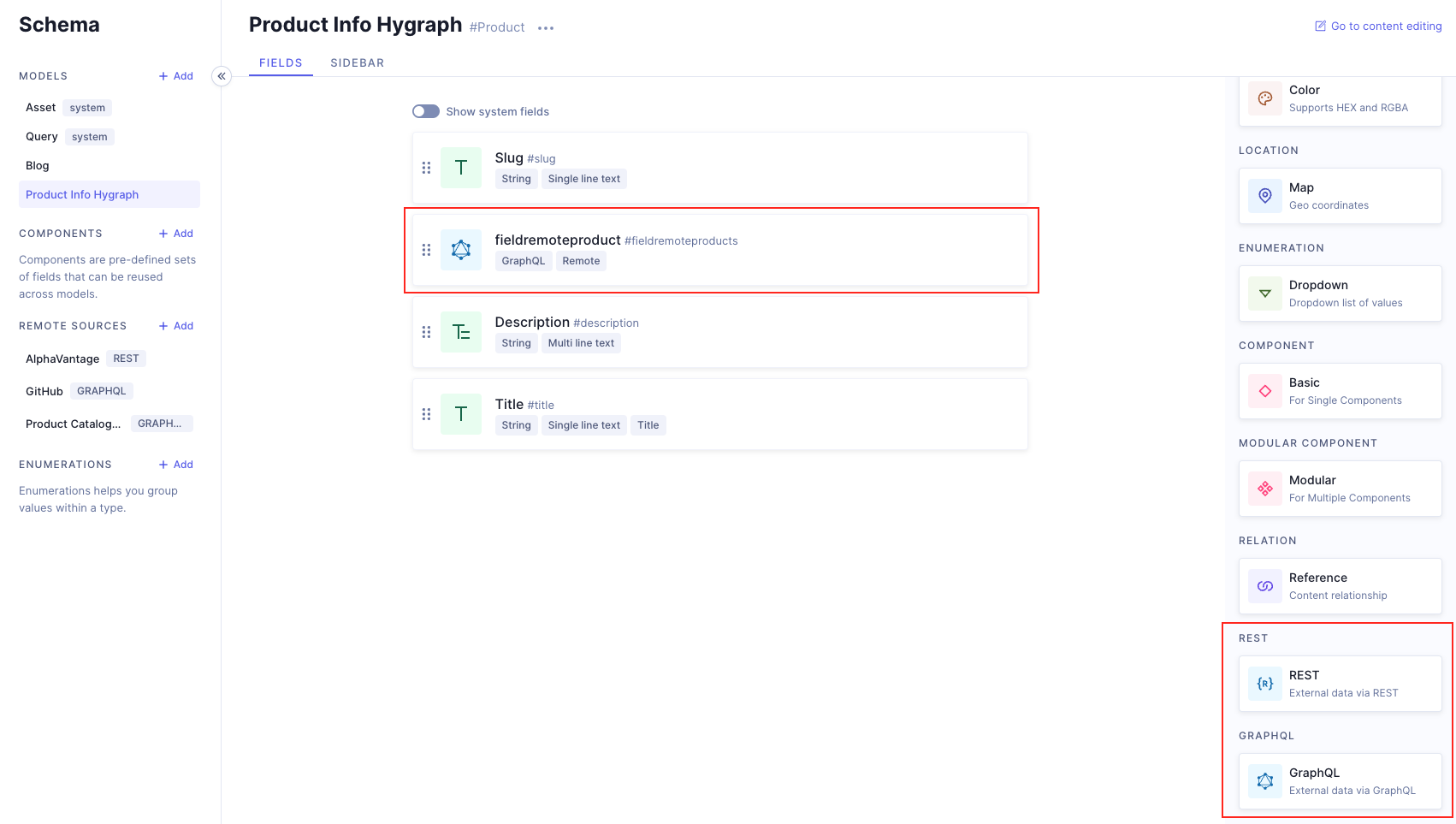 Remote field example
Remote field example
Requests will return information in Hygraph - Product model - as well as information in the Remote Source, called myCatalogue in our Product model for this example.
The frontend could then use this information received through the Hygraph Content API to display the product page enriched with the product catalogue.
#Top Level Remote Fields
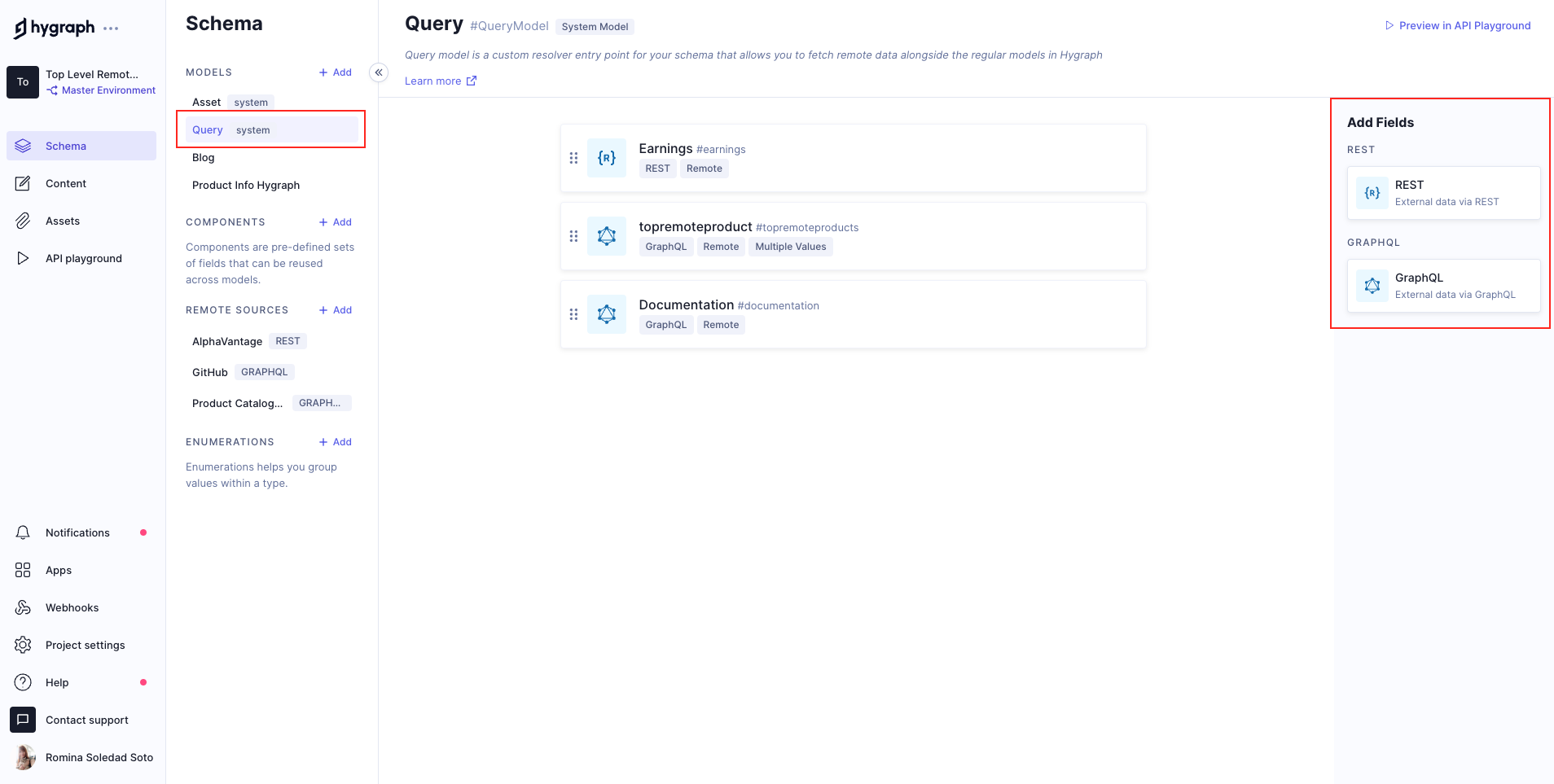
Top Level Remote Fields use the Query model, which is a custom resolver entry point for your schema that allows you to fetch remote data alongside the regular models in Hygraph.
You can find the Query model by navigating to the schema editor of your project.
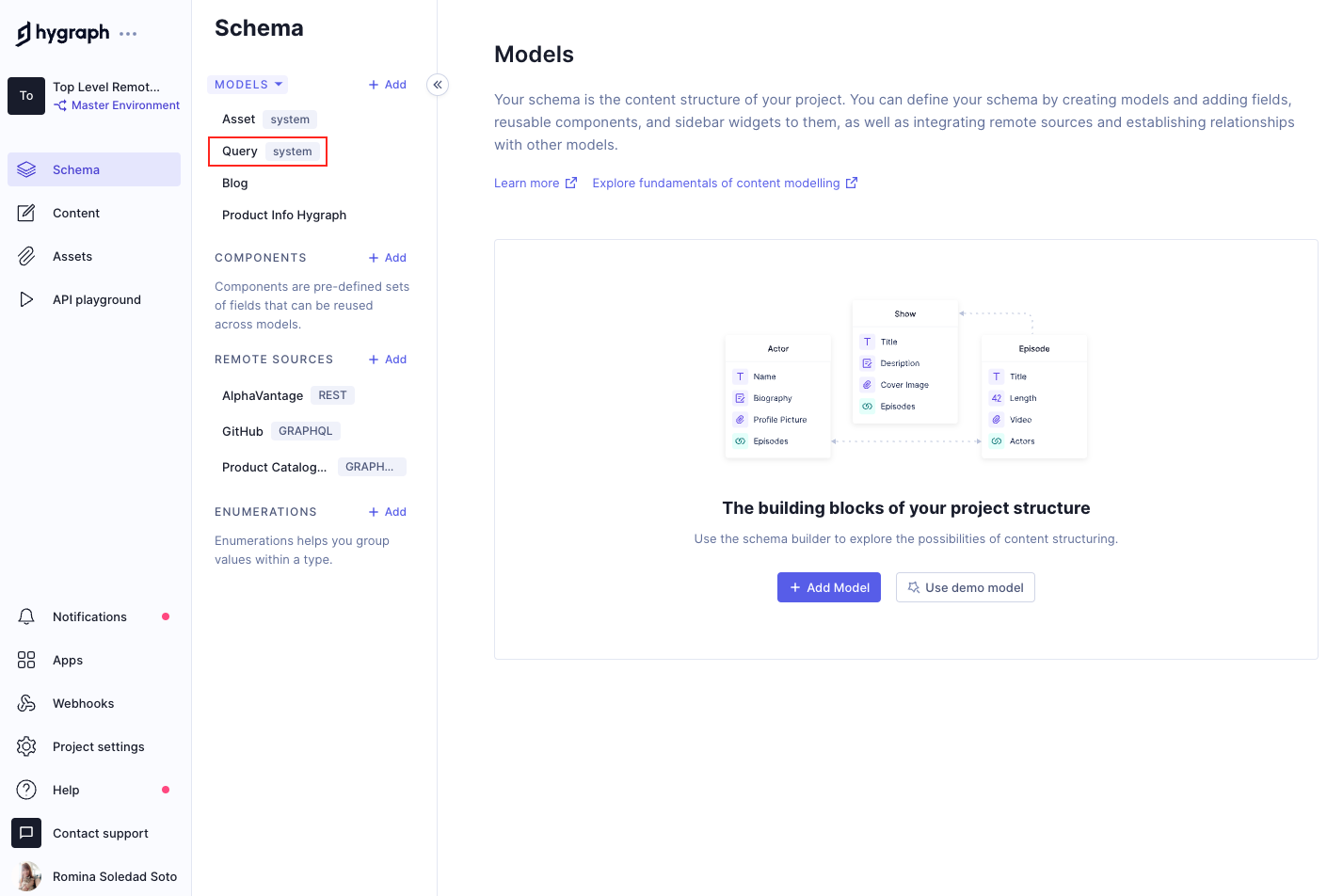 Query model
Query model
These Top Level Remote Fields exist in their own model in the schema - the Query model - and you can use them to go beyond the content enrichment case, by passing data that is unrelated to the content you have in your Hygraph project.
We called this the Query model, because in GraphQL query is the root type related to reading data.
This is also why adding Remote Fields to the Query model makes them available at the top level.
#What you can do with Top Level Remote Fields
-
You can use this model to pass data through our Content API without the need for it to be associated to a Hygraph content entry. In other words, you can use this model as a top-level entry point to fetch external data.
-
Take advantage of our Content Federation capabilities by integrating more systems and using them independently from their Hygraph content.
#Possible use cases for Top Level Remote Fields
- Data ownership needs to stay within the external system rather than being mirrored into another system.
- You are working with a multi-layered infrastructure, where data enrichment happens before the data reaches Hygraph.
- Your website makes calls to APIs that are not related to Hygraph.
- You are working on a project where not all content entries need enrichment.
#Create Top Level Remote Fields
- Create a Remote Source by following our Remote Sources creation flow.
- Select the
Querysystem model in your project schema. - Add a Remote Field to the
Querymodel using the Remote Source you created onstep 1. Please follow the adding remote data flow.
#Query Top Level Remote Fields
Top Level Remote Fields can be queried outside the context of a model.
In the following example, product is not a model, but a Top Level Remote Fields, completely unrelated to Hygraph content.
Instead of just enriching content that is in Hygraph, you can use the Hygraph API as a passthrough layer, where your frontend makes requests to APIs that don't relate to Hygraph.
With this Content Federation feature, you can use Hygraph to pipe everything through to your frontend without the need of making two separate requests.
Let's compare this to fetching information from within a model:
In this case, the Remote Field is related to the Products model, and it only fetches data related to it.
#Example 1: Top Level Remote Fields
This example shows a product information content entry that fetches the product catalogue from an external API, unretaled to Hygraph.
Besides the data that lives in Hygraph inside a regular model called Product information - Slug, Title, Description - you can fetch a product catalogue from an external API through a Remote Source that you add to the Query model as a Remote Field.
 Query model - Top Level Remote Fields example
Query model - Top Level Remote Fields example
Requests will return information in Hygraph - Product model- as well as information in the Remote Source, called fieldremoteproduct in our Query model for this example.
The frontend could then use this information received through the Hygraph Content API to display the product page along with a product catalogue sourced from an external API.
#Example 2: e-commerce platform
This video tutorial covers adding a remote source to Hygraph and creating Top-Level Remote Fields to pull in data from the external e-commerce platform, BigCommerce.